Maintaining Water Quality in Aquaponics: Tips and Best Practices
Introduction to Urban Aquaponics
In the heart of bustling cities, where space is limited and fresh food can be costly, urban aquaponics emerges as a revolutionary solution. By combining aquaculture (fish farming) with hydroponics (soilless plant cultivation), urban aquaponics creates a sustainable, closed-loop system that efficiently produces fresh vegetables and fish in city environments. This innovative approach to urban agriculture not only maximizes space but also conserves resources and reduces food miles, making fresh, healthy food more accessible to city dwellers.
As urban populations continue to grow, traditional farming methods struggle to meet the demand for fresh produce while minimizing environmental impact. Urban aquaponics addresses these challenges by utilizing available spaces such as rooftops, basements, warehouses, and vertical farms. With advancements in technology, these systems can now be fully automated, reducing labor costs and optimizing efficiency. Additionally, integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, can further enhance sustainability by lowering energy consumption.

How Urban Aquaponics Works
Urban aquaponics operates on a symbiotic relationship between fish and plants, creating a self-sustaining ecosystem. The process involves several key steps:
- Fish Production: Fish are raised in tanks where they produce waste, mainly in the form of ammonia-rich excretions.
- Biofiltration: Beneficial bacteria convert ammonia into nitrites and then into nitrates, a nutrient source essential for plant growth.
- Plant Cultivation: Plants absorb these nutrients through their roots, effectively filtering and purifying the water.
- Water Recirculation: The clean water is then returned to the fish tanks, ensuring a continuous loop of nutrient cycling.
This cycle minimizes waste, conserves water, and eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers or pesticides. The result is a highly productive, eco-friendly farming method that can thrive in urban settings such as rooftops, basements, and even abandoned industrial spaces.
Benefits of Urban Aquaponics
1. Maximizing Space in CitiesTraditional farming requires extensive land use, which is scarce in urban areas.
Urban aquaponics systems, however, can be designed to fit within confined spaces, such as:
- Rooftop Gardens: Transforming underutilized rooftops into productive farms.
- Indoor Vertical Farms: Utilizing shelving units and LED lighting to grow plants in stacked layers.
- Underground & Basement Farms: Repurposing abandoned buildings and underground spaces for food production.
By integrating these systems into existing infrastructure, cities can increase their local food supply without needing additional land.
2. Water Conservation and Sustainability
Urban aquaponics is one of the most water-efficient farming methods available. It uses up to 90% less water than traditional soil-based agriculture because water is continuously recycled. Since evaporation and runoff are minimized, these systems are particularly advantageous in regions facing water shortages.
Additionally, aquaponic farms can integrate rainwater harvesting systems, further reducing dependency on municipal water supplies and enhancing sustainability.
3. Chemical-Free and Organic Food Production
Since aquaponics relies on a natural ecosystem where fish and plants support each other, there is no need for synthetic fertilizers or pesticides. This results in:
- Healthier, organic produce with higher nutritional value.
- Sustainably farmed fish free from antibiotics and chemicals.
- Reduced environmental impact, as chemical runoff into waterways is eliminated.
4. Year-Round Harvesting and High Productivity
Traditional outdoor farming is subject to seasonal changes, but urban aquaponics can function year-round by incorporating:
- Controlled indoor environments using LED grow lights and temperature regulation.
- Greenhouse structures that optimize light exposure and climate conditions.
- Automated nutrient monitoring to ensure plants receive the exact nutrients they need at all times.
This ensures a continuous food supply, even in extreme climates where traditional farming is difficult.
5. Reduction in Carbon Footprint
Most urban areas rely on food imported from rural farms, leading to high carbon emissions due to transportation. By growing food within city limits, urban aquaponics:
- Reduces food miles and associated fuel consumption.
- Decreases greenhouse gas emissions from logistics and refrigeration.
- Provides fresher, locally sourced food to communities, reducing storage and packaging needs.
Setting Up an Urban Aquaponics System
Step 1: Choosing the Right Location
Selecting an optimal site is crucial for a successful urban aquaponics system. Potential locations include:
- Rooftops: Ideal for maximizing sunlight exposure.
- Indoor Spaces: Warehouses, basements, and garages can be transformed into fully controlled environments.
- Community Centers: Shared spaces that promote urban food production and local engagement.
Step 2: Selecting Fish and Plants
Careful selection of fish and plant species ensures system efficiency and productivity.
- Fish Options: Tilapia, catfish, trout, perch, and koi are popular choices due to their adaptability and fast growth.
- Plant Options: Leafy greens (lettuce, kale, spinach), herbs (basil, mint, cilantro), and fruiting crops (tomatoes, peppers, strawberries) thrive in aquaponic systems.
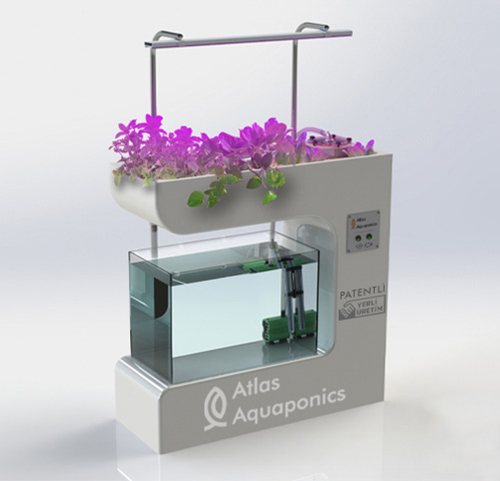
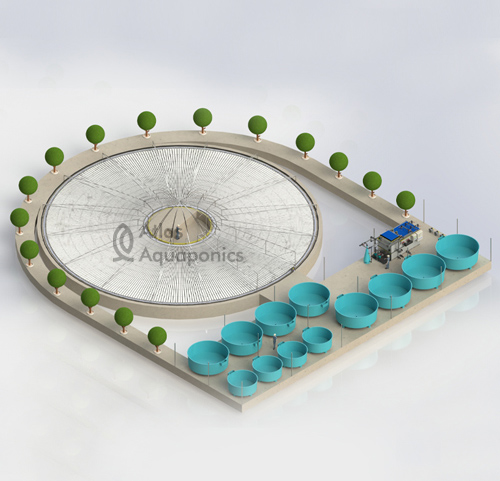
Step 3: Essential System Components
Every urban aquaponics setup requires key components:
- Fish Tank: Where fish are raised and nutrient-rich waste is produced.
- Grow Beds: Where plants absorb nutrients from the water.
- Biofilter & Mechanical Filter: Convert fish waste into usable plant nutrients and remove solid waste.
- Water Pumps & Aeration System: Ensures continuous water flow and oxygenation.
Challenges and Solutions in Urban Aquaponics
1. Limited Space & Scalability
- Solution: Implement vertical farming and stacking systems to maximize yield per square foot.
2. Energy Consumption
- Solution: Use LED grow lights, energy-efficient pumps, and integrate solar power to reduce operational costs.
3. High Initial Investment
- Solution: Seek funding from grants, local government initiatives, or crowdfunding campaigns.
4. Technical Knowledge Requirements
- Solution: Offer community training programs and online resources to educate new urban farmers.
The Future of Urban Aquaponics
Urban aquaponics is rapidly gaining traction as a sustainable solution to food security and climate change. Future advancements include:
- Smart Automation & IoT Integration: AI-driven nutrient monitoring and automated system controls.
- Expansion of Community-Based Aquaponics: Urban gardens and co-op farming initiatives.
- Increased Government Support: Policies that encourage urban agriculture and sustainability programs.
Conclusion
Urban aquaponics is more than just a farming method—it’s a transformative movement towards a greener, more resilient future. By integrating aquaponics into city environments, we can reduce environmental impact, enhance food security, and create healthier communities.
Are you ready to join the urban farming revolution? ContactAtlas Aquaponics today to learn how you can set up your own aquaponics system in the city!c